Acute vs. Chronic Lung Disease: What's the Difference? | CMI Health
Our lungs are a vital component of a complex system, constantly expanding and contracting to expel carbon dioxide and move oxygen into our bodies. Lung disease can happen when there are problems in any part of our complex respiratory system. Knowing the early signs of lung disease and the differences between respiratory illnesses can help you receive treatment before the disease becomes serious or even life threatening. Knowledge is powerful, especially when it comes to your health. Keep reading to find out what the difference is between chronic and acute lung disease, and how we can treat these conditions.
Acute Lung Disease
Acute illnesses develop suddenly and last a short time, often only a few days or weeks. They are typically caused by infection or injury. Acute illnesses may require urgent or short-term care but do improve upon receiving treatment. For example, if a person were to get into a car accident and break a bone, that would be considered an acute injury. Acute medical problems can be caused by chronic conditions and may be healed without curing the chronic illness.
There are many types of acute lung diseases, ranging from Pneumonia to SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome). Despite the treatability of acute lung diseases, they can still potentially become severe or even fatal if there is no proper intervention.

Examples of Acute Lung Diseases
- Pneumonia
- SARS
- Bronchitis
- Respiratory Infection
- COVID-19
- ACS (acute chest syndrome)
- ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome)
Symptoms & Treatment
Symptoms can vary for acute illnesses, as there is a wide range of causes and severity of acute lung conditions. For some acute lung conditions, symptoms will go away on their own without the need for medical intervention. Generally, deciding on the treatment and care for a patient with acute lung disease is based on whether it was brought on by viral infection, a traumatic event, or some other scenario and how serious the symptoms are.
Common Symptoms
- Fever
- Rapid heart rate
- Chest or back pain
- Coughing and shortness of breath
- Extreme fatigue and/or dizziness
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Sore throat
- Sinus congestion

As you may imagine, the treatments for acute respiratory conditions differ just as much as the symptoms do. They range from taking an over-the-counter drug for congestion to having to go to the emergency room or even ending up in a short-term hospital stay. Thankfully, most people with acute conditions quickly recover and return to enjoying their normal day-to-day life. Staying up to date with vaccinations that protect you against infectious respiratory diseases like COVID-19 and pneumonia can help protect people against acute lung conditions, and potentially more profound consequences.
For some acute lung diseases, treatment must be aggressive and fast-acting to prevent the condition from getting any worse. For example, ACS can progress very quickly which is why it's crucial to administer intravenous (IV) fluids, oxygen therapy, and sometimes even blood transfusions in the initial stages. The length of treatment for more serious acute illnesses can vary, and routine blood tests and oxygen level monitoring might be necessary to manage one’s health while on the mend.
Chronic Lung Disease
Chronic conditions develop slowly and may worsen over an extended period of time, such as months to years. They are long-lasting, persistent illnesses that are typically caused by genetics or unhealthy lifestyle behaviors. Environmental factors such as second-hand smoke or long-term exposure to industrial pollutants can also cause a chronic lung condition. Unfortunately, chronic diseases cannot be cured, but symptoms can be controlled with proper health management. Monitoring a chronic condition through self-management can keep symptoms from getting worse and improve one’s quality of life.

Examples of Chronic Lung Diseases
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Emphysema
- Lung cancer
- Pulmonary hypertension
Symptoms & Treatment
For some chronic diseases, symptoms can start out as mild and unsuspecting. With a mild cough or shortness of breath, one may think they might simply have the common cold. That is until these symptoms persist and worsen over time. This is why it’s important to know the warning signs and to see a doctor if even mild health problems are not resolving themselves.
Common Symptoms
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- A cough lasting more than a month
- Labored breathing
- Chest tightness
- Coughing up blood
- Blue-tinted lips
- Swelling of the ankles, feet, or legs
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, the American Lung Association recommends seeing a doctor immediately.

It is no secret how difficult chronic lung diseases can cause life to be for patients and their families. Luckily, there are many options for those that are affected by chronic lung diseases today, such as being able to track daily lung health with a digital spirometer to checking into a pulmonary rehabilitation center for long-term care. Quality of life is so important, and with the right treatments and medications, patients can regain control and enjoy an active lifestyle again.
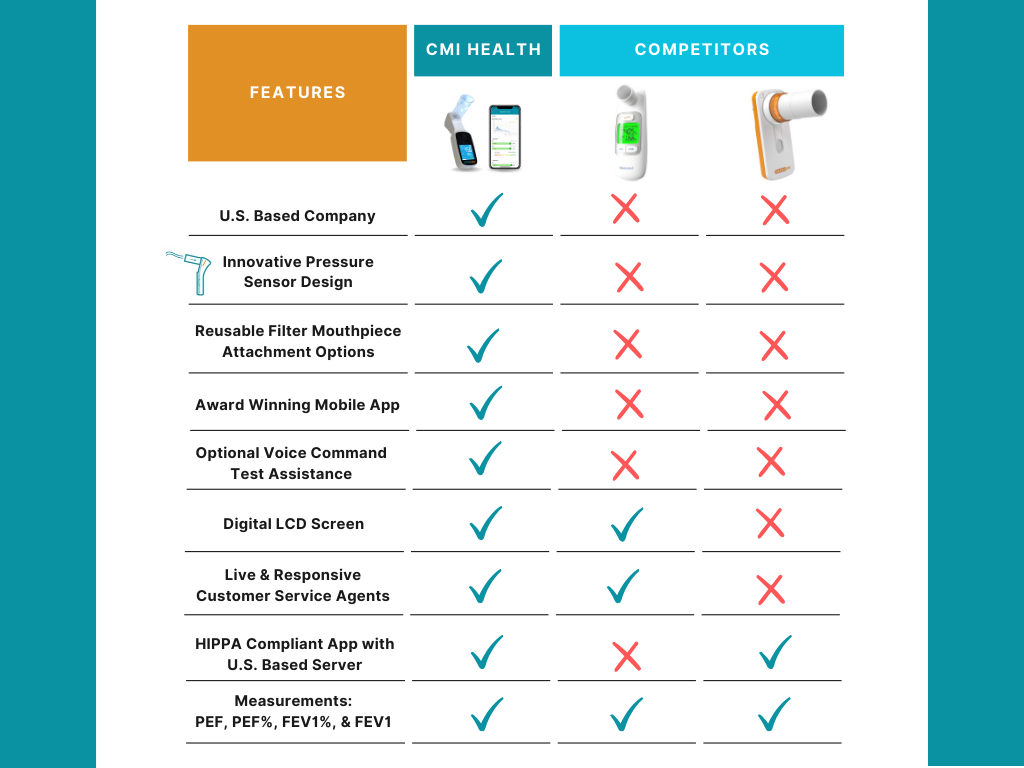
Making a healthcare plan with a trusted physician is crucial to treat a chronic condition; common medications that are prescribed to help manage lung diseases are antibiotics, vaccinations, anti-viral and anti-inflammatory drugs. Often, patients say that these types of medications are lifesavers. Patients can also partake in oxygen therapy and breathing exercises to further improve their lung health. Additionally, medical tools such as inhalers and spirometers are great for quick and easy treatments that one can do from the comfort of their own home. To learn more about spirometers and how they can help manage lung disease, click here.
Chronic lung diseases do not have to just be managed through doctor visits and medications; patients can also make beneficial lifestyle changes to offset the severity of these diseases. Things like eating a healthy diet, exercising, physical therapy, and refraining from smoking and alcohol or drug abuse can have a significant impact on one’s health. Click here to learn more about monitoring and managing lung health.
Still have questions? Feel free to contact us at info@cmihealth.com or call us at 888-985-1125 (ext. 1).


























Leave a comment